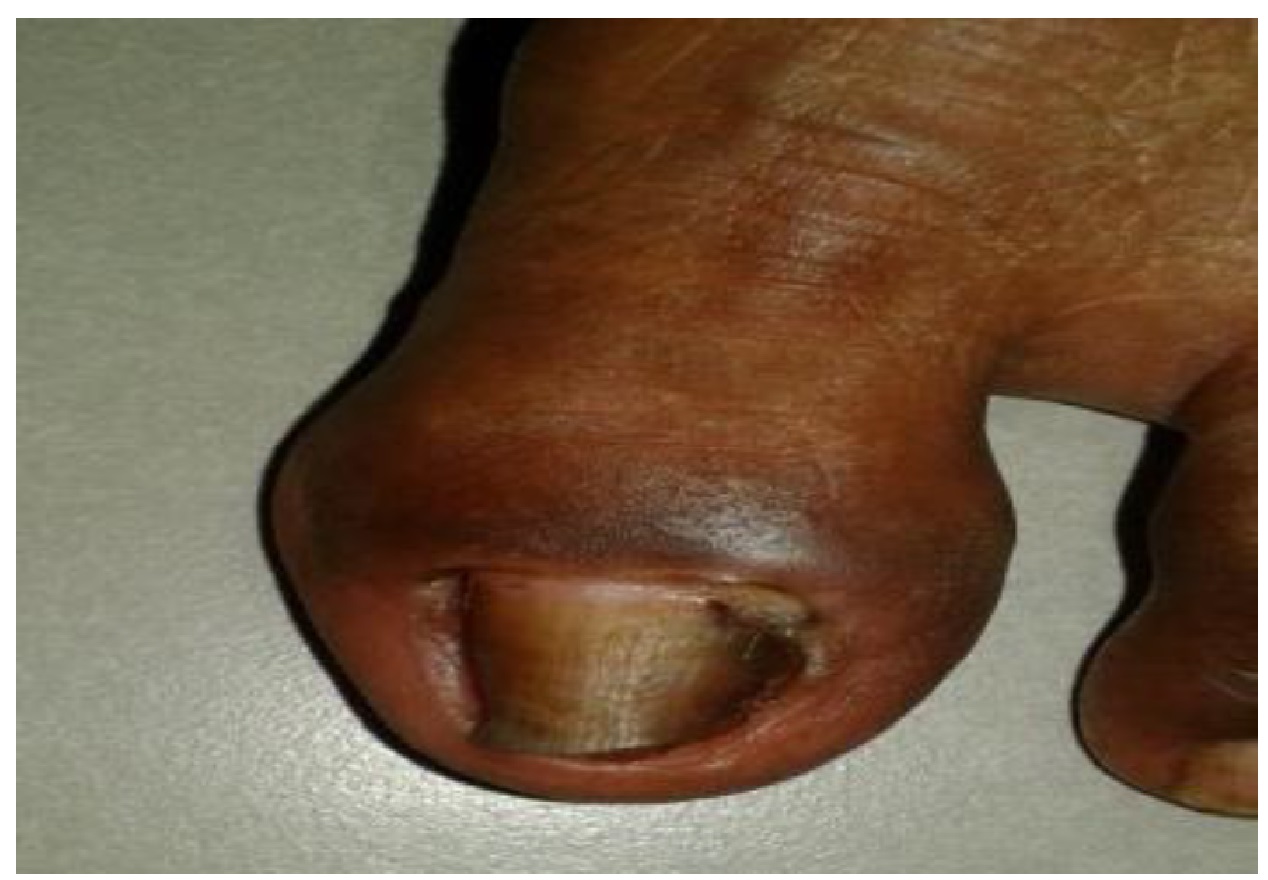
Effect of Jalukavacharana in Nail Bed Infection - A Single Case Study
Keywords:
Ayurveda, Kunakha, Nail bed infection, Jalaukavacharana, Case studyAbstract
In Ayurveda all type of nail infections is referred to as Kunakha. Word ‘Ku’ means ‘Bad’ and ‘Nakha’ means nail. A single case study showing Kunakha condition, which had resistant to therapy in contemporary science, induces encouraging results after the administration of external and palliative treatment (Shaman Chikitsa). Administration of Ayurveda treatment (external and internal) consecutively for 45 days had yielded good results in clinical symptoms as well as significant improvement in cosmetic view. The Shothahara, Rakta Prasadaka, and Strotoshodhaka properties of this remedy successfully subside the pathological features and improve the normal appearance of nail.
Downloads
References
Introduction to paronychia. Available from: https://www. Google.com/search?q=paronychia&rlz=1C1OKWM_ e n I N 7 9 0 I N 7 9 0 & o q = p a r o n y & a q s = c h r o m e. 0.0j69i57j0l3j69i61.9239j0j4&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8. [Last accessed on 2021 Dec 28].
Susruta. Susruta Samhita, Nibandhasangraha commentary of Dalhana Acharya. nyayachandrika of Gayadasa In:Hindi translation by Krishna Takral, 2nd part- sarir,chikitsa and Kalpa stana. Kshudraroga chikitsitam. Varanasi: Chowkhamba orientalia; Reprint 2014.p.394.
Agnivesa. Caraka Samhita revised by Caraka and Drdhabala with the Ayurveda Dipika Commentary of Chakrapanidatta. In: Vaidya Jadavji Trikamji Acharya, (Editor). Svayathu chikitsitham. Varanasi: Chowkhamba Krishnadas Academy; reprint 2015.p.490
Hiren N Ravel and AB Thakar.Role of Rakthamokshana by Jaluakavacharana and Siravedhana in the Mangemnt of Vicharchika (Eczema). Ayu. 2012.Jan Mar;33(1):68-72
Divya Kajaria. Text book of Panchakarma with illustrated picture. Rakthamokshana. Varanasi: Chaukambha Sanskrit Bhawan; second edition. reprint 2018.p.363