The Effect of 3-week’s Yoga therapy program on clinical outcomes in patients with Parkinson’s disease
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21760/jaims.7.10.8Keywords:
Parkinson disease (PD), integrated approach of yoga therapy (IAYT), Motor symptoms, behavioral symptoms, neuropsychiatric symptoms, conventional therapy.Abstract
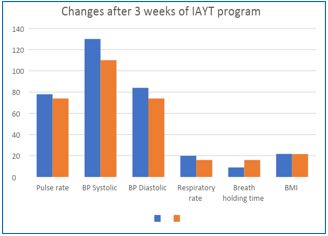
Background: Parkinson's disease, according to the WHO, has a variety of non-motor side effects in addition to its motor symptoms (cognitive impairment, mental health disorders, pain, and other sensory disturbances). The progression of these symptoms and their implications affects functioning and quality of life greatly, resulting in high rates of impairment and care demands, as well as stress and strain on caregivers. Material & Methods: A total of 31 PD patients were included in this investigation. The Integrated Approach of Yoga Therapy was applied to all patients who met the inclusion criteria (IAYT). Parameters were taken twice, once on the day of admission and other when they were leaving the residence on completion of the program. Data was evaluated using a pre-test and post-test design. Dependent Variable: Pulse rate, Respiratory rate, Systolic Blood Pressure, Diastolic Blood Pressure, Breath Holding time and BMI. Results: A total of 31 subjects participated in the study 31 subjects completed the study. After 21 days of integrated Yoga therapy program, it showed that significant reduction in (P< 0.05) in Systolic and diastolic Blood pressure, respiratory rate and significant improvement is seen in breath holding time (BHT), but there were no changes in BMI (P> 0.05). Conclusion: The three-week yoga programmed was able to dramatically enhance clinical results in Parkinson's disease and self-reported medication reduction without aggravating symptoms.
Downloads
References
Olanow CW, Tatton WG. Etiology and pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease
Launch of WHO’s Parkinson disease technical brief. (2022, June 14). Launch of WHO’s Parkinson Disease Technical Brief. Retrieved October 11, 2022, from https://www.who.int/news/item/14-06-2022-launch-of-who-s-parkinson-disease-technical-brief
Mackenzie, I. R. A. (2001). The pathology of Parkinson's disease. BC Medical Journal, 43(3), 142-147.
About Parkinson’s | Parkinson’s Europe. (n.d.). About Parkinson’s | Parkinson’s Europe. Retrieved October 2, 2022, from https://www.parkinsonseurope.org/about-parkinsons
A. (2018, July 26). Age, smoking and lack of fitness increase risk of Parkinson’s. Parkinson’s Life. Retrieved October 11, 2022, from http://parkinsonslife.eu/age-smoking-lack-fitness-increase-risk-parkinsons/
Parkinson’s Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments | National Institute on Aging. (2022, April 14). National Institute on Aging. Retrieved October 11, 2022, from https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/parkinsons-disease
Boland, D. F., & Stacy, M. (2012). The economic and quality of life burden associated with Parkinson's disease: focus on symptoms. American Journal of Managed Care, 18(7 Suppl), S168-175.
Bureau, United States Census. (2010).). (Morris, M. E. (2000). Movement disorders in people with Parkinson's disease: A model for physical therapy. Physical Therapy, 80(6), 578-597.
Sabate M, Gonzalez I, Ruperez F, Rodriguez M (1996) Obstructive and restrictive pulmonary dysfunctions in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sci 138: 114-119.
Garber CE, Friedman JH. Effects of fatigue on physical activity and function in patients with Parkinson's disease. Neurology. 2003;60:1119–24.
Ellis, T., Boudreau, J. K., Deangelis, T. R., Brown, L. E., Cavanaugh, J. T., Earhart, G. M., … Dibble, L. E. (2013). Barriers to exercise in people with Parkinson Disease. Physical Therapy, 93(5), 628-36.
Ni, M., Mooney, K., & Signorile, J. F. (2016). Controlled pilot study of the effects of power yoga in Parkinson’s disease. Complementary Therapies in Medicine, 25, 126–131. doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2016.01.007
Morris, M. E. (2000). Movement disorders in people with Parkinson's disease: A model for physical therapy. Physical Therapy, 80(6), 578-597.
Liu W, McIntire K, Kim SH, Zhang J, Dascalos S, et al. (2006) Bilateral subthalamic stimulation improves gait initiation in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Gait Posture 23: 492-498.
Jankovic, J. (2008). Parkinson's disease: Clinical features and diagnosis. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 79(4), 368-376.
Saint-Cyr JA, Taylor AE, Lang AE. Neuropsychological and psychiatric side effects in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Neurology. 1993;43(12 Suppl 6):S47–S52.
Cutson TM, Laub KC, Schenkman M (1995) Pharmacological and nonpharmacological interventions in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Phys Ther 75: 363-373.
Roland, K. P. (2014). Applications of yoga in Parkinson's disease: A systematic literature review. Research and Reviews in Parkinsonism, 4, 1-8.
Reijnders, J. S., Ehrt, U., Weber, W. E., Aarsland, D., & Leentjens, A. F. (2008). A systematic review of prevalence studies of depression in Parkinson’s disease. Movement Disorders, 23(2), 183-189; quiz 313.
Oken BS, Kishiyama S, Zajdel D, Bourdette D, Carlsen J, Haas M, et al. Randomized controlled trial of yoga and exercise in multiple sclerosis. Neurology, 2004; 62: 2058–2064.
Hennard J. A protocol and pilot study for managing fibromyalgia with yoga and meditation. Int J Yoga Therap. 2011;21:109–21.
(Tran MMD. Effects of hatha yoga practice on the health-related aspects of physical fitness. Prev Cardiol. 2001;4(4):165–170).
Vogler J, O’Hara L, Gregg J, Burnell F. The impact of a short-term Iyengar yoga programme on the health and well-being of physically inactive older adults. Int J Yoga Therapy. 2011;21:61–72.
Colgrove Y, Sharma N, Kluding P. Effect of yoga on motor function in people with Parkinson’s disease: a randomized, controlled pilot study. J Yoga Phys Ther. 2012;2:112.
Colgrove Y, Sharma N, Kluding P. Effect of yoga on motor function in people with Parkinson’s disease: a randomized, controlled pilot study. J Yoga Phys Ther. 2012;2:112.
Hoehn MM, Yahr MD (1967) Parkinsonism: onset, progression and mortality. Neurology 17: 427-442.
Goetz CG, Poewe W, Rascol O, Sampaio C, Stebbins GT, et al. (2004) Movement Disorder Society Task Force report on the Hoehn and Yahr staging scale: status and recommendations. Mov Disord 19: 1020-1028.
Colgrove YS, Sharma N, Kluding P, Potter D, Imming K, et al. (2012) Effect of Yoga on Motor Function in People with Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized, Controlled Pilot Study. J Yoga Phys Ther 2:112. doi:10.4172/2157-7595.1000112
Nagarathna R, Nagendra H. Integrated Approach of Yoga Therapy for Positive Health. Bangalore: Swami Vivekananda Yoga Prakashana; 2008. p. 8-20.
Nagarathna R, Nagendra HR. Integrated Approach of Yoga Therapy for Positive Health. Bangalore: Swami Vivekanand Yoga Prakashana; 2004.
Villacres, M. D. C., Jagannathan, A., Nagarathna, R., & Ramakrishna, J. (2014). Decoding the integrated approach to yoga therapy: Qualitative evidence based conceptual framework. International journal of yoga, 7(1), 22.
Boulgarides, L. K., Barakatt, E., & Coleman-Salgado, B. (2014). Measuring the effect of an eight-week adaptive yoga program on the physical and psychological status of individuals with Parkinson's disease. A pilot study. International Journal of Yoga Therapy, 24(1), 31-41.
Oken BS, Kishiyama S, Zajdel D, Bourdette D, Carlsen J, Haas M, et al. Randomized controlled trial of yoga and exercise in multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 2004;62:2058–64.
Scott M, Masterson M, Elmer L, et al. P2.160 The effects of a yoga program on Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2009;15(Suppl 2):S133.
Roland, K. P. (2014). Applications of yoga in Parkinson's disease: A systematic literature review. Research and Reviews in Parkinsonism, 4, 1-8.