An anatomical study of Guda Marma and its clinical importance
Keywords:
Guda, Anus, Pureeshvaha Srotas, Sadhyopranhara Marma, Guda MarmaAbstract
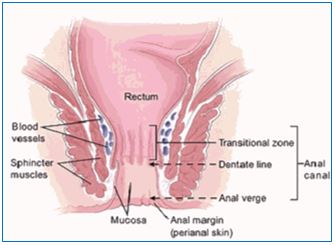
Nowadays owning to the sedentary life style with almost negligible or irregular physical activities as well as improper diet, frequency of several diseases and disorders has increased significantly. Guda (Anus) thus is implied in context of disease since ages and plays a very important role in the physical wellbeing of human body. The terminal part of large intestine and Moola of Pureeshava Srotas is known as Guda. It is one of the Karmendriyan. Charak has mentioned that Guda is one of the Koshtangas. Guda is defined as the passage through which excretion of faeces takes place and is located in the pelvic region and Charaka recognized two parts in it i.e., Uttara Guda and Adhara Guda. It is one among nine Bahirmukhasrotas located in pelvic region. Total length of Guda is 4½ Angula. There are 3 sphincter situated inside the Guda placed one above the other at a distance of 1½ Angula from each other and are named as Pravahini, Visarjini and Samvarni. Pureeshdhara Kala is related to Guda and it is Moola of Pureeshvaha Srotas and also is Sadhyopranhara Marma. Guda thus is implied in context of disease since ages and plays a very important role in the physical wellbeing of human body. Objective of the study are comprehensive literary review of Guda Marma with correlation of anatomical features described in Ayurveda to contemporary science. Data related to Guda Sharira and diseases were collected from various classics.
Downloads
References
Sharma SP. Shareera Sthana chapter 7 verse 24 Astanga Sangraha with Sashilekha Sanskrit commentary of Indu. 2nd ed. Varanasi (India): Chaukambha Orientalia; 2008; p.326.
Sushruta Samhita Dalhana Acharya Virachita Nibhandhasangraha vyakhya, Vaidya Yadavaji Trikamaji Acharya, Choukhambha Surabharati Prakashana, Varanasi, reprint 2010. Page no: 369.
Acharya YT. Shareera Sthana chapter 6 verse 26 Sushruta Samhita with Nibhandhasangraha commentary of Dalhanacharya. Reprint ed. Varanasi (India): Chaukambha Sankrit Sansthan; 2010.;p.55.
Bhaskar Govind Ghamekar, Sushruta Samhita, Ayurveda sandipika, Hindi, vyakhya, 3rd edition 1997, Meherechandre Lakashamendas (Sanskrit) 6/44.
Bhaskar Govind Ghamekar, Sushruta Samhita, Ayurveda sandipika, Hindi, vyakhya,3rd edition 1997, Meherechandre Lakashamendas (Sanskrit) 6/14.
Bhaskar Govind Ghamekar, Sushruta Samhita, Ayurveda sandipika, Hindi, vyakhya,3rd edition 1997, Meherechandre Lakashamendas (Sanskrit) 6/24.
Sushruta Samhita with Hindi commentary by Kaviraj Ambikadutta Shastri, Part-1, page no. 67, Sharir Sathan 6/4, by Chaukhambha Sanskrit Sansthan, 2011.
Sushruta Samhita with Hindi commentary by Kaviraj Ambikadutta Shastri, Part-1, page no. 67, Sharir Sathan 6/5, by Chaukhambha Sanskrit Sansthan, 2011.
Sushruta Samhita with Hindi commentary by Kaviraj Ambikadutta Shastri, Part-1, page no. 67, Sharir Sathan 6/8, by Chaukhambha Sanskrit Sansthan, 2011.
Caraka Samhita of Agnivesha revised by Caraka and Drdhabala with an introduction by Vaidya Samrata Sri Satyanarayana Sastri, Chikitsa sthana part 2 published by Choukamba Bharati Academy, Varabasi reprint:2001, pg no:716 pp:1208.
Caraka Samhita of Agnivesha revised by Charaka and drdhabala with an introduction by Vaidya samrata Sri Satyanarayana Sastri, Siddhisthana, part 2, published by Choukamba Bharati Academy, Varanasi reprint:2001, pg no:1050 pp:1208.
William, L. P., & Warwick R. (1980). Editor. Gray’s Anatomy. 36th ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 1578, 1358, 1359, 288-292, 293-314.
Romanes, G. J., (1996). Editor. Cunningham’s Manual of Practical Anatomy, 15thed. New York: Oxford university press, 2, 298, 11-77, 200-210, 3, 346, 3-27, 35-92, 135-165.