A clinical study on the effect of Lodhradi Kashaya on Madhumeha with special reference to Diabetes Mellitus (Type-2)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21760/jaims.8.11.4Keywords:
Madhumeha, Lodhradi Kashaya, Metformin, Comparative studyAbstract
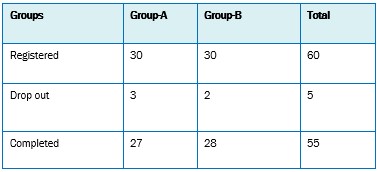
Introduction: Ayurveda describes Prameha as a disease entity which involves a number of diseases with various physical and chemical changes in urine. Madhumeha is included under Vatik Prameha where astringency is associated with sweetness in urine. The manifestation of metabolic abnormality as well as urinary tract pathology are included in two symptoms: Prabhuta Mutrata (excessive urination) and Avila Mutrata (urine turbidity). Sedentary life style, indulgence of Kapha-meda Vardhaka Ahara, avoidance of regular exercise, day sleep indicate Santarpanajanya origin of the disease. Methods: Lodhradi Kashaya with Lodhra, Musta, Katphal and Haritaki as described in Vasavarajeeyam is taken for this clinical study on 60 patients and its efficacy was compared with a standard drug metformin. Results: During the study it was found that both Lodhradi Kashaya and Metformin provided significant result in improving Signs and Symptoms like polyuria, turbid urination, Polydipsia, polyphagia, burning sensation, numbness, weakness, lassitude, pruritus, muscle cramps, and increased sweating. The test of significance shows that both the trial drug and control drug were highly significant at 0.1% level with p-value <0.001 to improve glycosuria, FBS, PPBS and HbA1c in patients. Comparative analysis of the effectiveness of Lodhradi Kashaya and metformin w.r.t. objective sign and symptoms showed that both the treatments are almost equally effective to improve glycosuria, FBS, PPBS and HbA1c while Lodhradi Kashaya gives better clinical improvement than metformin in long term use in Diabetes. Lodhradi Kashaya is an efficient anti diabetic drug.
Downloads
References
Acharya YT, editor. (Reprint Ed.) Nibandhasamgraha Tika of Dalhana and Nyaya Chandrika Tika of Gayadas on Susruta Samhita of Susruta, Nidan Sthana, Prameha Nidanam, Chapter 6, Verse 23. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Orientalia; 2014. p. 293.
Joshi JS, editor. (3rd Ed.) Abhidhana Ratnamala of Halayudha Bhatta. Lucknow: Uttar Pradesh Hindi Sansthan; 1993. p. 544.
Acharya YT, editor. (Reprint Ed.) Nibandhasamgraha Tika of Dalhana and Nyaya Chandrika Tika of Gayadas on Susruta Samhita of Susruta, Nidan Sthana, Prameha Nidanam, Chapter 6, Verse 23. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Orientalia; 2014. p. 290.
Gaur BL, editor. (1st Ed.) Ayurveda Dipika Tika of Chakrapanidatta on Charak Samhita of Agnivesha, Vol-II, Nidan Sthan, Prameha Nidan: Chapter 4, Verse 19. New Delhi: Rastriya Ayurveda Vidyapeetha; 2014. p. 121.
Gaur BL, editor. (1st Ed.) Ayurveda Dipika Tika of Chakrapanidatta on Charak Samhita of Agnivesha, Vol-II, Nidan Sthan, Prameha Nidan: Chapter 4, Verse 44. New Delhi: Rastriya Ayurveda Vidyapeetha; 2014. p. 130.
Harrison’s Principle of Internal Medicine. 19th edition. Page 2399.
Ramachandran A, et al. High prevalence of Diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance in India; National Urban Diabetes Survey. Diabetologia. 2001;3(8):488-94.
IDF Diabetes Atlas 2010.
Pandey G. (1st Ed.) Commentary on Vasavarajeeyam of Vasavaraj, 9th prakarana. Varanasi: Chaukhamba Krishnadas Prakashan; 2010. p. 286.
Mahanta NR, et al. Lodhradi Kashaya as a Potent Antidiabetic Agent: A Drug Review. World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research. 2022;11(3):1115-1129.
Singh, & Ramachandra Reddy, Konduru. (2017). Review on Lodhradi Kashaya: All-rounder remedy for Diabetes mellitus patients. Indian journal of traditional knowledge. 16. 100-106.
Singh R, et al. Management of diabetic complications: A chemical constituent-based approach. J Ethnopharmacol 2013;150;51-70.
Bramhankar RB, Reddy KRC, Trigunayat A. Hypoglycemic effect of Lodhradi Kashaya Ghanavati in streptozotocin –induced hyperglycemia in rats. International Journal of Green Pharmacy. Oct-Dec 2015. 9(4)/241-245.
Singh VK, Reddy KRC. Management of Diabetes mellitus and its complications by Lodhra: A review. International Journal of Ayurvedic Medicine. 2015;6(4):305-309.
N Singh, et al. Phyto-pharmacotherapeutics of Cyperus rotundus Linn. (Motha): An overview. Indian Journal of Natural Products and Resources. Vol. 3(4), December 2012, pp. 467-476.
Gupta et al. Biological and pharmacological properties of Terminalia chebula Retz. (Haritaki)- an overview. Int J Pharm Sci. Vol 4, Suppl 3, 62-68.
Joshi et al. Myrica nagi: a review on active constituents, biological and therapeutic effects. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. Vol 4, Suppl 5, 38-42.