Ergonomics in work situations of Ayurvedic therapists working in Vaidyaratnam Ayurveda College, Ollur, Trissur
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21760/jaims.9.2.7Keywords:
Ayurvedic therapists, Cognitive ergonomics, Ergonomics, MSD, Organisational ergonomics, Physical ergonomicsAbstract
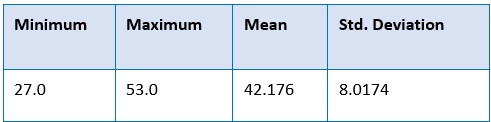
Introduction: Ergonomics is defined as the process of designing or arranging workplaces, products and systems so that they fit the people who use them. Physical, organizational and cognitive are the three types of ergonomics. Aims and Objectives: To assess the prevalence of Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSD) in Ayurvedic therapists working in, Vaidyaratnam Ayurveda College, Ollur, Trissur. Materials and Methods: A Descriptive cross sectional study was done. 17 therapists in VACH Ollur were surveyed consecutively regarding symptoms of Musculoskeletal disorders mainly LBA, neck pain, shoulder pain, knee pain and heel pain. Data were collected by using questionnaires and were analysed using appropriate statistical methods. Results: Out of 17 therapists, 52.9 % were females. Highest frequency of MSD was seen in the age group of 46-55 years. 80 % of the therapists were working more than 20 years. 64.5 % were suffering from LBA, 29.4% were suffering from neck pain, 23.8% were suffering from shoulder pain, 41.2% were suffering from knee pain and 17.6 % were suffering from heel pain. Discussion: Present study shows that MSD are common among therapists. Improper posture for different procedure can be the reason. Adhering to the principles of physical and cognitive ergonomics can prevent risk factors of developing MSD.
Downloads
References
Edwards C, Fortingo N, Franklin E. Ergonomics. [Updated 2022 Jul 28]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK580551/
Gupta A, Bhat M, Mohammed T, Bansal N, Gupta G. Ergonomics in dentistry. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2014 Jan;7(1):30-4. [PMC free article] [PubMed].
Waters TR, Dick RB. Evidence of health risks associated with prolonged standing at work and intervention effectiveness. Rehabil Nurs. 2015 May-Jun;40(3):148-65. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Andersen LL, Vinstrup J, Sundstrup E, Skovlund SV, Villadsen E, Thorsen SV. Combined ergonomic exposures and development of musculoskeletal pain in the general working population: A prospective cohort study. Scand J Work Environ Health. 2021 May 01;47(4):287-295. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Baba, N.H. & Daruis, Dian. (2016). Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI) among computer users: A case study in telecommunication company. Malaysian Journal of Public Health Medicine. 2016. 48-52.