Role of Ayurvedic medicines with Panchakarma therapy in SLE w.s.r. to Aamvata
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21760/jaims.9.3.36Keywords:
Systemic lupus erythematosus, SLE, Pitta, Autoimmune, Panchakarma therapy, AamvataAbstract
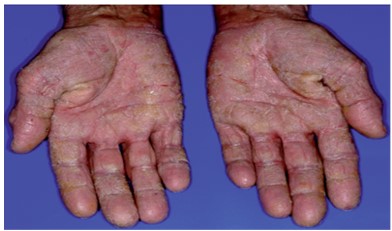
Background: Autoimmune disorders occur when the body’s immune system is working hard to defend against potentially precarious substances our bodies such as allergens, toxins, infection or food but does not identify the difference between the invaders and own body cells. SLE is an autoimmune disease in which organs, tissues and cells undergo damage, mediated by tissues binding auto antibodies and immune complexes. SLE affects heart, joints, skin, lungs, blood vessels, liver, kidney and nervous system. Due to Piita Pradhantwa in SLE it can be correlated with Pitta Anubandhi Amavata as both are systemic autoimmune disease having involvement of mainly Pitta Dosha. Materials and Methods: A male patient with complaints of pain in multiple joints with swelling, recurrent mouth ulcers, weakness all over the body and erythematous rashes on both hands with some discharge came to OPD of PTKLS Hospital and diagnosed as Amavata and admitted in IPD of the Hospital and treated according to Ayurveda Protocol including oral medications and Panchakarma therapy. Result: Patient got symptomatic relief. Details of this will be discussed in full paper. Discussion: In Ayurveda, symptoms of Vata Kapha Anubandhi Amavata can be correlated with RA and symptoms of Pitta Anubandhi Amavata can be correlated with SLE as there is involvement of Pitta Dosha and Rakta Dhatu in SLE.
Downloads
References
D. P. D'Cruz, M. A. Khamashta, and G. R. Hughes, “Systemic lupus erythematosus,” The Lancet, vol. 369, no. 9561, pp. 587–596, 2007.
Cojocaru M, Cojocaru IM, Silosi I, Vrabie CD. Manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Maedica (Bucur). 2011 Oct;6(4):330-6. PMID: 22879850; PMCID: PMC3391953.
Madhavnidan, hindi commentary by Yadunandan Upadhyay, amavata nidan, chaukhamba prakashan, poorvardha, 509-51
SLE Criteria [Internet]. [cited 2024 Apr 16]. Available from: https://sliccgroup.org/research/sle-criteria/
Charaka Samhita, Sutra Sthana, Atreyabhadrakapiya adhyaya, 26 /31Available from: http://niimh.nic.in/ebooks/echarak
Sanjay Kumar et al. “Review of Haridra Khand and its pharmaceutical preparation.” International Ayurvedic Medical Journal, vol. 11, no. 1, 2023, pp. 2232-2238
Dr Raja Singla, Dr Pankaj Sharma,Role of Panchtikta Kshira Basti in Management of Avascular Necrosis : A Case Study, IJRMST, July-December 2021, Vol 12, 115-120.