An experimental evaluation of Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Activity of Allium Cepa Linn. and Allium Ascalonicum Linn. - A comparative study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21760/jaims.9.5.7Keywords:
Allium cepa Linn, Allium ascalonicum Linn, Anti-inflammatory, AnalgesicAbstract
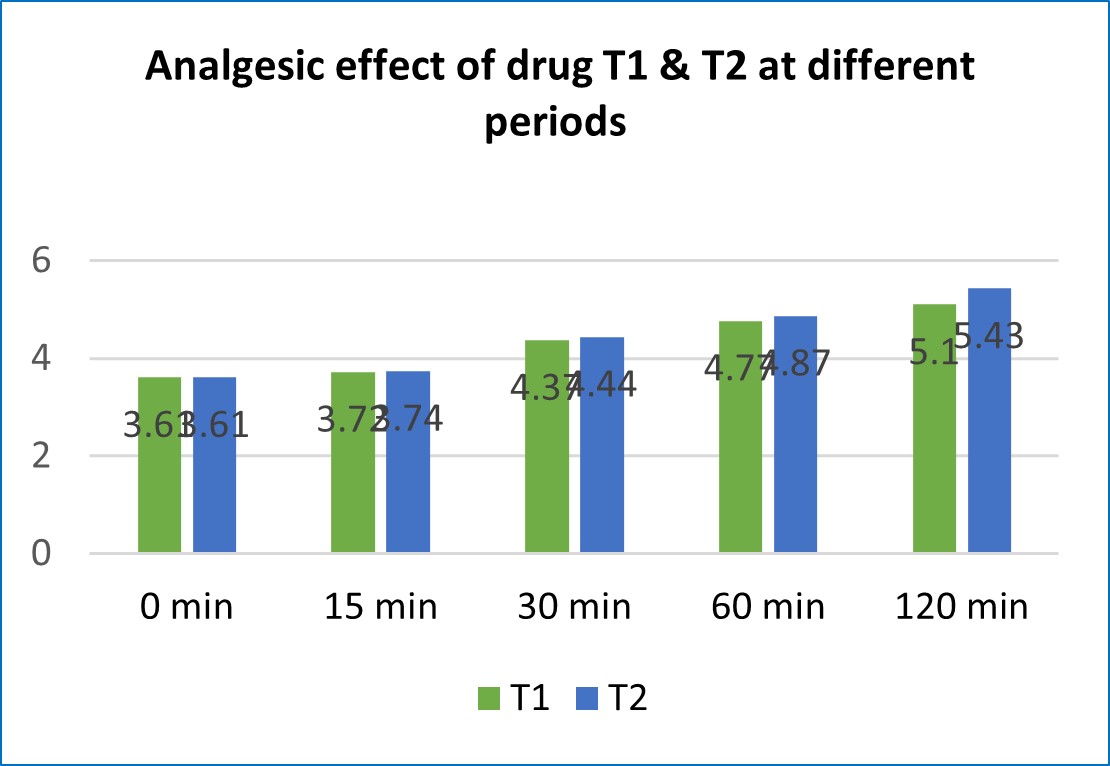
Introduction: The drugs possessing Vataghna property are much indicated in classics for managing Shotha and Vedana. Cost-effective, widely available, and potent drugs should be encouraged over costly ones. The present study was undertaken based on this, focusing on the bulb of Allium cepa Linn. & Allium ascalonicum Linn. to evaluate the anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities employing carrageenan induced paw oedema in wistar albino rats and hotplate tests in mice, respectively. Materials and Methods: Fresh juice of Allium cepa Linn. and Allium ascaloncum Linn. was given to rats and mice orally to observe anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity, and observed for a day. Anti-inflammatory activity was evaluated using carrageenan induced paw edema model in wistar albino rats. Analgesic activity was evaluated using Hot plate method in mice. Experimental animals were divided into 4 groups, Group A as control was given distilled water and; Group B with standard drug, Paracetamol suspension, Group T 1 as test drug 1 with Swarasa of Allium cepa Linn; and Group T 2 as test drug II with Swarasa of Allium ascalonicum Linn. as per the calculated doses respectively. Results: Animals treated with the test drugs showed a significant reduction in paw oedema and had analgesic effects compared to the control group. The result obtained was also assessed by a one-way-ANOVA test. Discussion: The experiment concludes that both the test drugs have anti-inflammatory and analgesic capabilities. However, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect was seen better in Allium ascalonicum Linn. than Allium cepa Linn. No adverse effects were noted in the study.
Downloads
References
Sastry JLN. Dravyagunavijnana. Varanasi. Chaukhambha Orientalia.2003. P 564
Fang XX, Zhai MN, Zhu M, He C, Wang H, Wang J, Zhang ZJ. Inflammation in pathogenesis of chronic pain: Foe and friend. Mol Pain. 2023 Jan-Dec;19: Inflammation in pathogenesis of chronic pain: Foe and friend - PMC (nih.gov)
Nair AB, Jacob S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J Basic Clin Pharm. 2016 Mar;7(2):27-31. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human - PMC (nih.gov)
Nair AB, Jacob S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J Basic Clin Pharm. 2016 Mar;7(2):27-31. doi: 10.4103/0976-0105.177703. PMID: 27057123; PMCID: PMC4804402.
Hegde.PL. A text book of dravyaguna vijnana. 1st ed. New delhi:Chaukambha Publications; 2011
Batiha GE, Beshbishy AM, Ikram M, et al. The Pharmacological Activity, Biochemical Properties, and Pharmacokinetics of the Major Natural Polyphenolic Flavonoid: Quercetin. Foods. 2020;9(3):374. Published 2020 Mar 23.
José M. et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of alkaloids: a twenty-century review. Rev. bras. farmacogn. [online]. 2006, vol.16, n.1 [cited 2021-05-18], pp.109- 139. Available from: <http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0102695X2006000100020&lng=en&nrm=iso>. ISSN 1981-528X.
Alexandra M.S. et.al. Terpenes as possible drugs for the mitigation of arthritic symptoms – A systematic review, Phytomedicine, Volume 57, 2019, Pages 137-147,ISSN 09447113,https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2018.10.028
Sapna D. Desai, Dhruv G. Desai, Harmeet Kaur. 2009. Saponins and their biological activities. PharmaTimes.41.13-16
Khan, H., Pervaiz, A., Intagliata, S. et al. The analgesic potential of glycosides derived from medicinal plants. DARU J Pharm Sci 28, 387–401 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40199-019-00319-7