Rejuvenation of Ayurveda: Major Obstacles and A Way Forward
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21760/jaims.9.10.29Keywords:
Ayurveda, AYUSH, Chronic health conditions, DispensariesAbstract
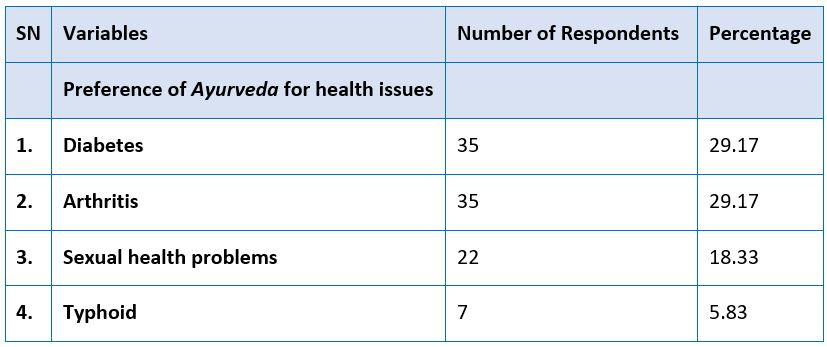
Ayurveda is again reviving and receiving a great deal of attention as a result of the role it plays in meeting the primary health care needs. The primary purpose of this study was to determine the role that Ayurveda plays in the delivery of health care to the rural masses as well as to investigate the issues that stand in its way. Exploratory research design was used to collect the information. The study found that Ayurveda is playing an important role in combating chronic diseases such as diabetes, arthritis, etc. Unsuccessful past experiences and affordability served as two major pull factors for respondents to turn to traditional medicine. Government dispensaries opened under AYUSH are encountering several challenges, such as inadequate infrastructure and a scarcity of doctors and medications. It is imperative for the government to prioritise and increase funding for traditional systems of medicine and organise training programmes for traditional practitioners with the aim of delivering healthcare services that are both secure and economically efficient.
Downloads
References
Dharmuche, Lata Changev. (2018). The folk medicine of Goa (Unpublished doctoral thesis). Gulbarga University: Karnataka.
Islam, Md. Nazural. (2009). Reviving Ayurveda in modern India: Prospect and challenges. International Review of Modern Sociology, 35(1), 137-147.
Kurup, P.N.V. (2001). Ayurveda. In Ranjit Roy Chaudhury & Uton Muchtar Rafei (Eds.), Traditional Medicine in Asia (pp 3-16). Delhi: SEARO Regional Publications.
Kusinitz, Marc. (1991). The Encyclopaedia of Health: Folk medicine. New York: Chelsea House Publishers.
Shah, N.C. (1982). Herbal folk medicines in Northern India. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 6: 293-301.
Srinivasan, R., & Sugumar, V. Raji. (2017). Spread of traditional medicines in India: Results of national sample survey organization’s perception survey on use of AYUSH. Journal of Evidence-Based Complementary & Alternative Medicine, 22(2), 194-204.
WHO Global Report on Traditional and Complementary Medicine, 2009.
https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/chandigarh/punjab-ayurvedic-dispensaries-running-sans-medicines/articleshow/71499396.cms / Accessed on 20.12.2023
https://www.hindustantimes.com/punjab/12-of-16-posts-of-ayurvedic-doctors-lying-vacant-in-faridkot-district/story-Go/ Accessed on 17.04.2024
https://www.tribuneindia.com/news/jalandhar/lack-of-staff-medicines-ail-ayurvedic-dispensaries-118712/ Accessed on 20.06.2024