Identification of Dry Ayurvedic Herbs (Roots and Stems) Through Ai/Computer Vision Technology
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21760/jaims.10.1.12Keywords:
Ayurvedic herbs, Convolutional Neural Networks, Image recognition, Dataset, Validation accuracy, Dry herb identification, AI, Machine learningAbstract
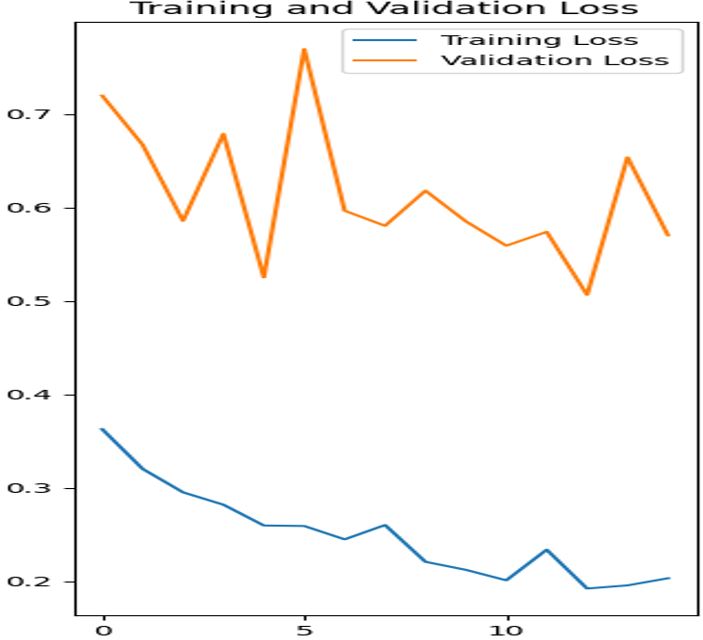
This study presents a novel AI-based approach for the identification and quality control of dry Ayurvedic herbs using Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). The model was developed to identify 43 types of dry Ayurvedic herbs, comprising 14 stems and 29 roots, based on visual features such as texture, colour, and shape. A dataset of 4,300 high-resolution images was curated using smartphones, and preprocessing techniques like normalization and augmentation were applied to enhance model robustness. The CNN model, with four convolutional layers (32 to 256 filters) and dropout layers, was designed to efficiently extract hierarchical features while preventing overfitting. The model achieved high training accuracy (94%) but encountered challenges in validation accuracy (85%), indicating difficulties in generalization. A confusion matrix revealed strong performance for distinct herb species but highlighted misclassifications among visually similar herbs. This study demonstrates the potential of AI and computer vision technologies to automate herb identification and quality control, reducing human dependency and errors. The system is deployable on mobile devices or servers, offering practical applications in the pharmaceutical and Ayurvedic industries, with significant benefits for consumer confidence and the authenticity of herbal products. Future work will focus on expanding the dataset, refining preprocessing methods, and utilizing enhanced computational resources, such as GPUs and cloud computing, to improve model scalability, efficiency, and generalization.
Downloads
References
Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI). Guidance note on cinnamon [Internet]. CCASIA; 2014 Mar 10 [cited 2024 Oct 19]. Available from: https://www.fssai.gov.in/upload/advisories/2018/04/5ac47df86d178Guidance_Note_Cinnamon_CCASIA_10_03_2014.pdf.
World Health Organization. Quality Control Methods for Medicinal Plant Materials. Geneva: WHO; 1992.
Government of India, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Department of AYUSH. The Ayurvedic Pharmacopeia of India. New Delhi: Government of India.