Internet Gaming Disorder - Ayurvedic Perspective
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21760/jaims.8.5.35Keywords:
Internet gaming disorder, reward system, antireward system, Prajnaparadha, Asathmya Indriyarthasamyoga, ManovegaAbstract
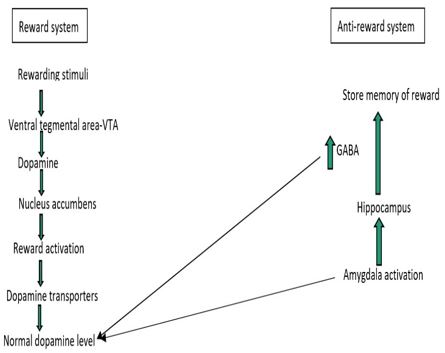
Internet gaming is the most entertaining activity of current generation, especially of the young adolescents. Gaming provides, a sense of accomplishment through a virtual reality platform and finally, intense degree of fun. Anyhow Spending too much time and avoiding all necessary activities for gaming leads to Internet gaming addiction. Due to the negative consequences in the behavioral and cognitive components and the alteration in reward and anti-reward system it is considered as a disorder in DSM 5 and ICD 11. Symptoms include anxiety, depression, preoccupied thoughts, irritability, playing games to feel better, insomnia, feeling of emptiness, inability to control the gaming, restlessness, fantasies and dreams about the game. In this review, the concept of gaming disorder in Ayurveda is concentrated in the light of Manovikaras/ Manasika Bhava, Prajnaparadha and Asathmya Indriyartha Samyoga. Management approaches are discussed in preventive and curative aspects. Management can also be done by assessing the dosha predominance and severity in each stage.
Downloads
References
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition, Text Revision. American Psychiatric Association, Inc., Arlington, VA 2022.
Sabrina Schenk, Robert K. Lech, Boris Suchan, Games people play: How video games improve learning, Behavioural Brain Research, Volume 335,2017, Pages 208-214,ISSN 0166-4328
Ivory JD. A brief history of video games. In The video game debate 2015 Aug 27 (pp. 1-21). Routledge.
Undavalli VK, Rani GS, Kumar JR. Prevalence of internet gaming disorder in India: a technological hazard among adolescents.,2020
Orsolya Király, Marc N Potenza, Zsolt Demetrovics, Gaming disorder: current research directions, Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences, Volume 47,2022
Kumar, Amit, Kalpana Sharma, Jayanti Jain, Noori Aara, and Vishal Sharma. "Repercussion of internet use and its ayurvedic restoration." (20210
Mamun MA, Griffiths MD. The psychosocial impact of extreme gaming on Indian PUBG gamers: the case of PUBG (Player Unknown’s Battlegrounds). International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction. 2021 Dec;19(6):2170-4.
Hellström C, Nilsson KW, Leppert J, Åslund C. Influences of motives to play and time spent gaming on the negative consequences of adolescent online computer gaming. Computers in human behavior. 2012 Jul 1;28(4):1379-87.
Petry NM, Rehbein F, Gentile DA, Lemmens JS, Rumpf HJ, Mossle T, et al. An international consensus for assessing internet gaming disorder using the new DSM-5 approach. Addiction. 2014.
Susrutha, Susruthasamhitha with Nibandhasamgraha commentary, utharathantra, Vaidya Jadavji Trikamji Acharya, Chaukhambha Sanskrit Sansthan, Varanasi, 2013, p. 690
Kuss, Daria & Griffiths, Mark. (2012). Internet Gaming Addiction: A Systematic Review of Empirical Research. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction. 10. 278-296. 10.1007/s11469-011-9318-5.
Teng Z, Pontes HM, Nie Q, Griffiths MD, Guo C. Depression and anxiety symptoms associated with internet gaming disorder before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: A longitudinal study. Journal of Behavioral Addictions. 2021 Apr 16;10(1):169-80.
Kuss DJ, Pontes HM, Griffiths MD. Neurobiological correlates in internet gaming disorder: a systematic literature review. Frontiers in psychiatry. 2018 May 8;9:166.
Shankara Bhashya, Adi Sankaracharya Commentary Srimad Bhagavad Gita 2/ 62 p.45
Cha. Sa. Acharya JT, editor. Agnivesha, Elaborated by Charaka and Dridhabala, Commentary by Chakrapani. Charaka Samhita,Sutra Sthana Varanasi: Chaukhamba Surbharati Prakashan; 2014, 7/52 p. 322.
Charaka. Samhita. Acharya JT, editor. Agnivesha, Elaborated by Charaka and Dridhabala, Commentary by Chakrapani.,ShariraSthana Varanasi: Chaukhamba Surbharati Prakashan; 2014, 1/101,p.120
Acharya Agnivesh, Charaka Samhita, revised by Charaka and Dradhabala, vidhyodhinihindi commentary by Pandit Kashinath Shastri and Pandit Gorakhanatha Chaturvedi, Shareersthana, Chaukhamba Bharti Academi, Varanasi, 2009. 1/126 p. 82
Sajjad C, Jayadevan CV, An uncontrolled clinical trial on the effect of Aswagandha choorna along with satvavajaya chikitsa in nomophobia and a cross sectional study among Ayurveda students of Kerala, 2020
Vagbhada. Ashtanga hridayam. Reprint 2010. [Prof. K. R. Sreekantamurthy, trans]. Vol. 2. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Krishnadas Academy Chikitsa sthana,7/20-23, p. 158
Maurya K, Dadhore S. wait & watch through yoga techniques to overcome tentative internet game disorder in adolescent groups.
Putchavayala CK, Singh D, Sashidharan RK. A perspective of yoga on smartphone addiction: A narrative review. Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care. 2022 Jun 1;11(6):2284-91.
Putchavayala CK, Singh D, Sashidharan RK. A perspective of yoga on smartphone addiction: A narrative review. Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care. 2022 Jun 1;11(6):2284-91.
Spindler B. Yoga therapy for fear: Treating anxiety, depression and rage with the vagus nerve and other techniques. Singing Dragon; 2018 Jun 21.