Evaluation the Accelerated Stability of Dadrughni Vati (Lepa) and Dadrughna Malahara: A Comparative Approach
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21760/jaims.10.3.15Keywords:
Shelf life, Stability Study, Dadrughni Vati (Lepa) (DL), Dadrughna Malahara (DM), ICH guidelinesAbstract
Introduction: The shelf life and stability of traditional herbal formulations are essential for their efficacy and safety. Stability studies of Dadrughni Vati (Lepa) (DL) and its modified form, Dadrughna Malahara (DM), have not been conducted. This study evaluates their shelf life under accelerated storage conditions per ICH guideline Q1A, analyzing organoleptic, physicochemical, microbial, and chemical stability parameters.
Methods: DL and DM were stored under accelerated conditions for six months, with stability assessments at 0, 3, and 6 months. Evaluations included organoleptic properties (color, texture, odor), physicochemical parameters (pH, extractive values, moisture content for DL; specific gravity, iodine value, acid value, viscosity, spreadability for DM), microbial contamination (total plate count, yeast and mold, pathogens), and chemical stability through HPTLC fingerprinting at 254 nm, 366 nm, and 540 nm. Shelf life was estimated using degradation curve analysis.
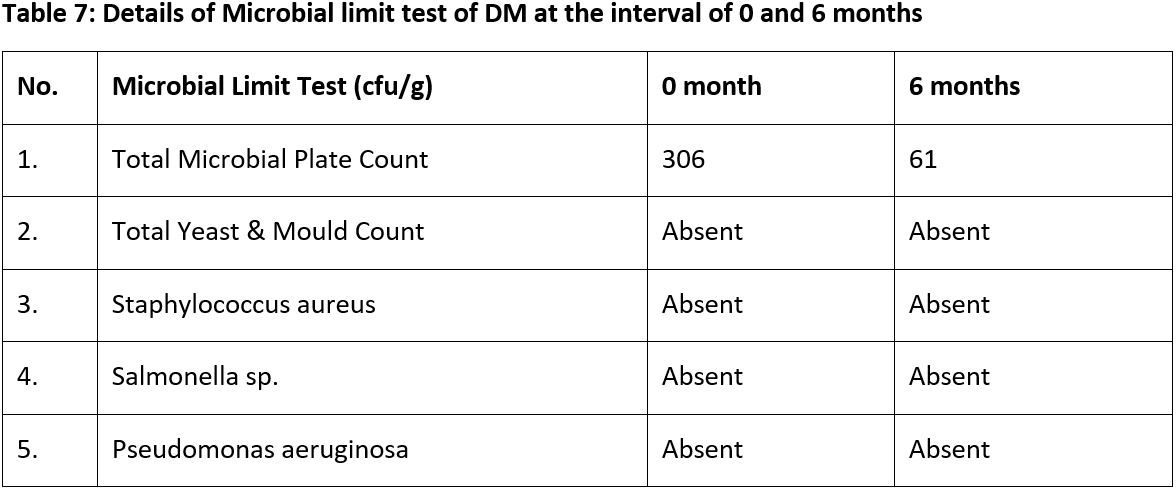
Results: Both formulations remained stable in organoleptic properties. DL exhibited changes in pH, extractive values, and moisture content, while DM showed increases in specific gravity, iodine value, and acid value. The microbial limit test confirmed pathogen-free status. HPTLC analysis indicated consistent chemical composition without significant degradation.
Conclusion: DL and DM demonstrated stability under accelerated conditions, with slight physicochemical variations. Shelf-life estimates suggest DL is stable for 6.89 years and DM for 3.59 years in climate zones III and IV, ensuring their quality and therapeutic efficacy.
Downloads
References
International Council for Harmonisation. Available from: https://www.ich.org. [Accessed 2024 Oct 8].
Gujarat Rajya Bheshaj Samiti. Bheshaj Samhita. Swasthya Mantralaya Gujarat Ahmedabad; 1966. Chapter 13. p. 745.
Khan MA, Khar RK. Stability studies on pharmaceuticals. J Pharm Sci. 2002;91(6):1330–40.
Harris et al. Impact of moisture on the stability of pharmaceutical products. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1996;22(8):779–87.
Fenn et al. The effect of temperature and humidity on ash content in mineral supplements. J Agric Food Chem. 2017;65(7):1421–8.
Santos et al. Microbial activity and its effect on the composition of ash in herbal remedies. Phytother Res. 2019;33(9):2290–6.
Santos et al. Solubility of bioactive compounds: Effects of pH and solvent environment. J Agric Food Chem. 2019;67(11):3132–40.
Chakraborty et al. Phase transitions and their influence on the stability of pharmaceutical products. J Pharm Sci. 2019;108(5):1658–67.
Dyer et al. Iodine value and the stability of oils and fats. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 2002;79(5):445–50.
Yadav KD et al. Preliminary physicochemical profile of Brahmi Ghrita. Ayu. 2013;34:294.
Gupta A et al. Impact of microbial contamination on the saponification value of lipids. Int J Chem Stud. 2017;5(2):919–22.
Bramucci et al. The effect of storage conditions on viscosity and spreadability of cosmetic formulations. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2019;41(2):130–7.
Dubey NK, Kumar A, Singh P, Shukla R. Microbial contamination of raw materials: A major reason for the decline of India’s share in the global market. Curr Sci. 2008;95(6):717–8.