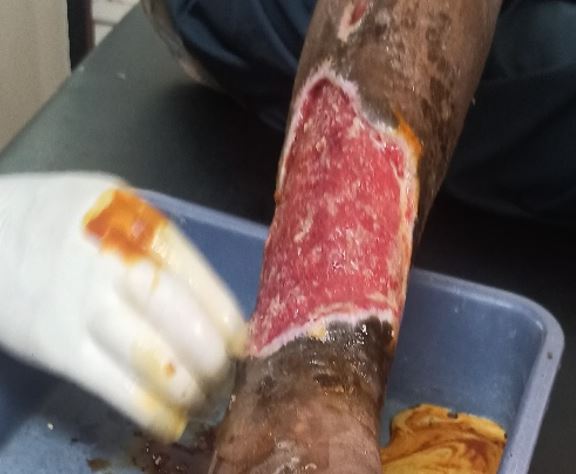
Therapeutic application of Honey in the management of Infected Diabetic Foot Ulcer - A Case Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21760/jaims.10.8.41Keywords:
Infected wound, Dushta Vrana, honey, wound healing, antibacterial property of honey, honey as wound dressingAbstract
Honey is gaining popularity as a dressing for chronic wounds. Existing literature attributes honey with a number of useful properties, such as a broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, deodorization, debriding and anti-inflammatory actions and stimulation of new tissue growth. Honey has been recognized for its medicinal properties since antiquity. Modern clinical research supports its efficacy in promoting wound healing and controlling infections due to its antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and wound-debridement properties. Case studies are being published increasingly which record positive outcomes with its use. Recent national media attention has featured the beneficial effects of honey in wound care and patients are beginning to request treatment. While honey may become a useful and widely accepted product for wound management in the future, the following case studies demonstrate that not all the expected beneficial effects are always realized in practice.
Downloads
References
Acharya VJT. Sushrut Samhita. Vol. 2. 8th ed. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Orientalia; 2005. p. 396.
Acharya VJT. Sushrut Samhita. Vol. 2. 8th ed. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Orientalia; 2005. p. 408.
Shukla AV, Tripathi RD. Charak Samhita. Vol. 2. 24th ed. Delhi: Chaukhambha Sanskrit Pratishthana; 2009. p. 520.
Shastri KA. Sushrut Samhita. Vol. 1. 15th ed. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Sanskrit Sansthan; 2019. p. 4.
Shastri KA. Sushrut Samhita. Vol. 1. 15th ed. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Sanskrit Sansthan; 2019. p. 18.
Molan PC. The role of honey in the management of wounds. J Wound Care. 2001;10(8):409–11.