Evaluation of Long-Term Glycemic Outcomes Following Ayurvedic Panchakarma Therapy and Lifestyle Intervention in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A One-Year Follow-Up Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21760/jaims.10.8.2Keywords:
Ayurveda, Panchakarma, Hyperglycemia, Metabolic syndrome, Glycemic control, HbA1c, Lifestyle modification, Diabetic neuropathy, Cardiovascular risk, Prameha, Madhumeha, Santarpanajanya VyadhiAbstract
Background: Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition marked by high blood sugar - the side effects of long-term allopathic treatment highlight the need for exploring safer, integrative therapies.
Methods: A retrospective, observational, single-centre study was conducted in Maharashtra, India between October 2021 and April 2024. Patients aged 18 years and above with a diagnosis of diabetes mellitus (HbA1c ≥6%) according to the American Diabetes Association and adherent to oral hypoglycemic agents who underwent treatment with the Comprehensive Diabetic Care Program were included in this analysis.
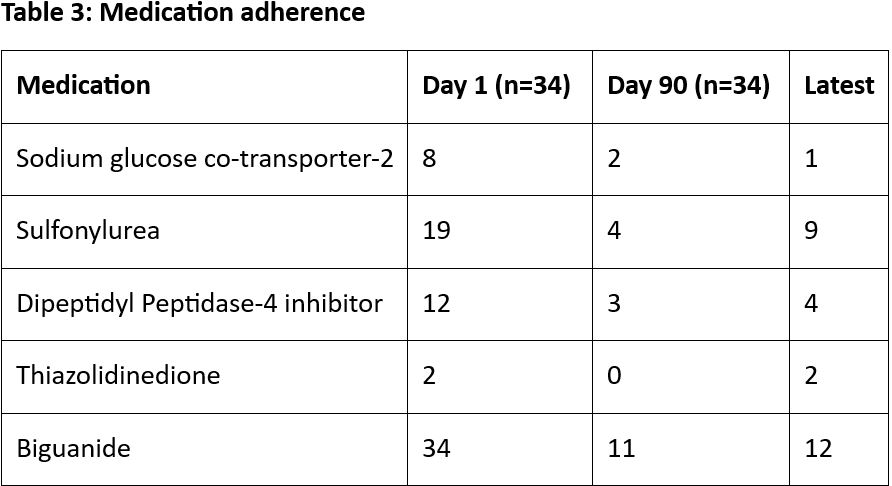
Results: Mean age of the study patients was 53.78 ± 11.08 years, of which 34 (68%) patients were male. Mean weight (day 1: 72.43 ± 12.38 kg, day 30: 70.45 ± 12.33 kg, day 60: 69.41 ± 12.15 kg, day 90: 69.15 ± 12.34 kg, and 1 year: 70.38 ± 12.26, p=0.00), body mass index (day 1: 27.51 ± 3.68, day 30: 26.76 ± 3.83, day 60: 26.43 ± 3.78, day 90: 26.31 ± 3.90, and 1 year: 26.78 ± 3.94, p=0.00), and abdominal girth (day 1: 96.54 ± 8.74 cm, day 30: 93.80 ± 8.98 cm, day 60: 92.14 ± 8.56 cm, day 90: 91.72 ± 8.59 cm, and 1 year: 92.84 ± 8.61 cm, p=0.00) improved at the follow-ups. Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) (day 1: 8.28 ± 2.10%, day 30: 7.22 ± 1.45%, day 60: 6.83 ± 1.02%, day 90: 6.55 ± 0.84%, and 1 year: 6.74 ± 0.81, p=0.00) also improved significantly at the follow-ups.
Conclusion: Integrated Ayurvedic management of type 2 diabetes mellitus over a 90-day period has proven highly effective in maintaining long-term glycemic control, even after 1-year of follow-up, whilst significantly reducing dependence on allopathic medications.
Downloads
References
Kumar A, Gangwar R, Zargar AA, Kumar R, Sharma A. Prevalence of diabetes in India: A review of IDF Diabetes Atlas 10th edition. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2024;20(1):e130423215752.
International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 7th ed. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation; 2015. Available from: http://www.idf.org/idf-diabetes-atlas-seventh-edition
Unnikrishnan R, Anjana RM, Mohan V. Diabetes mellitus and its complications in India. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016;12(6):357–70.
Pradeepa R, Mohan V. Epidemiology of type 2 diabetes in India. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2021;69(11):2932–8.
ElSayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR, Bannuru RR, Brown FM, Bruemmer D, et al. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of care in diabetes—2023. Diabetes Care. 2023;46(Suppl 1):S19–S34.
Sane R, Ghadigaonkar P, Chaure R, Jain S, Wahane S, Nadapude A, et al. Efficacy of Comprehensive Diabetes Care (CDC) management program in elderly male patients of type II diabetes mellitus: A retrospective study. Int J Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;3(2):29–34.
Rohit S, Imran S, Minal N, Tejaswini A, Rahul M. To study efficacy of Comprehensive Diabetes Care (CDC) management program in type II diabetic obese patients: An observational study. Int J Ayurveda Pharma Res. 2018;6(6):6–12.
Sane R, Naik M, Khair K, Mahajan H, Pawar D, Revandkar V, et al. Effect of Comprehensive Diabetes Care on glycaemic control with reduction in dependency of oral hypoglycaemic medicines in pre-obese diabetic patients: A retrospective study. Int J Curr Res Acad Rev. 2018;6(11):73–81.
Sane R, Mandole R, Amin G, Ghadigaokar A, Paranjape S. Effectiveness of Comprehensive Diabetes Care (CDC) in diabetic patients: An observational study. Int J Innov Res Med Sci. 2020;5(8):314–9.
Sane R, Mandole R, Amin G, Ghadigaokar P, Paranjape S, Gond B, et al. Role of Comprehensive Diabetes Care in known diabetes patients from western Mumbai region: An observational study. Int J Res Med Sci. 2020;8(8):3013–8.
Sane R, Mandole R, Amin G, Ghadigaokar A, Paranjape S, Wajage A, et al. Role of Comprehensive Diabetes Care in known diabetes patients from Pune region. Int J Curr Adv Res. 2020;9(8):22937–41.