Dosha-Dushya Sammurchana in Vatarakta: A Comparative View with Gout Pathophysiology
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21760/jaims.10.8.29Keywords:
Ayurveda, Vatarakta, Uttana and Gambhira, Gouty arthritisAbstract
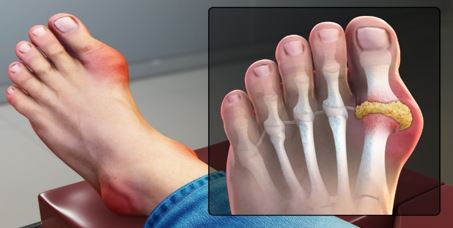
Health is an intricate concept that encompasses physical, physiological, mental, emotional, spiritual, and social well-being, all of which are deeply affected by dietary and lifestyle choices. Ayurvedic texts consistently highlight the vital importance of Ahara (diet) and Vihara (lifestyle) in maintaining Swasthya (health) and Vikara (diseases). This focus is particularly pertinent today, in light of the notable increase in metabolic disorders related to lifestyle. According to Ayurveda, Vatarakta is a disease that involves an imbalance of Vata Dosha that affects Rakta Dhatu. The Vata, whose pathways are impeded by Rakta, is further vitiated, contaminating the Rakta or blood. Vatarakta is a profound Vatavyadhi produced by Avarana (occlusion) disease. Vatarakta have two Avasthas i.e., Uttana and Gambhira. Uttana Vatrakta affects Twacha and Mamsa Dhatu whereas Gambhira mainly affects Asthi, Majjadi Gambhira Dhatu. One of the best and most significant methods for determining a disease's causes, prognosis, and diagnosis is Nidan Panchak. The five parts of Nidan Panchak are Purvarupa, Rupa, Upshaya, Samprapti, and Nidan. The primary and crucial diagnostic technique in Ayurveda is the Nidana Panchak. The symptoms of gout are very similar to those described in Vatarakta. Gout is a common type of arthritis caused by uric acid disruption, in which excess uric acid in the bloodstream forms crystals in the joint, causing acute pain, swelling, and stiffness. Different Ayurveda texts, journals, research papers, articles are referred to study the concept of Vatarakta and its usefulness in manifestation and sequelae of the Vatarakta
Downloads
References
Shastri K, Chaturvedi G. Charaka Samhita. Chikitsa Sthana, 29/11. Vol. 2. Varanasi: Chaukhamba Bharati Academy; 2001. p. 820.
Shastri KA. Sushruta Samhita. Varanasi: Chaukhamba Sanskrit Sansthan; 2007.
Gupta KA. Ashtanga Hridaya with Vidyotini Hindi Commentary. 14th ed. Varanasi: Chaukhamba Orientalia; 2003.
Tripathi BN. Madhava Nidana with Madhukosha Commentary. Vol. 1. Varanasi: Chaukhamba Surbharati Prakashan.
Shukla AV, Tripathi RD. Charaka Samhita (Agnivesha). Parts 1 and 2. 2nd ed. Varanasi:
Savitri, [co-authors not provided]. Innovative Ayurvedic Vivechana of Vata-Rakta – A Conceptual Study. WJPMR. 2020;6(4):50-3.
Agnivesha. Charaka Samhita. Chikitsa Sthana, 29/11. Varanasi: Chaukhamba Sanskrit Sansthan; 2002. p. 984.
Agnivesha. Charaka Samhita. Sutra Sthana, 26:86-87. 4th ed. Varanasi: Chaukhamba Sanskrit Sansthan; 1994. p. 362.
Agnivesha. Charaka Samhita with Ayurveda Dipika Teeka. Varanasi: Chaukhamba Sanskrit Sansthan; 2000. p. 29.
Longo DL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Jameson JL, Loscalzo J. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. 18th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Walker BR, Colledge NR, Ralston SH, Penman ID. Davidson’s Principles and Practice of Medicine. 20th ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone.
Walker BR, Colledge NR, Ralston SH, Penman ID. Davidson’s Principles and Practice of Medicine. 20th ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone.