Clinical Evaluation of Obenyl Tablet in the management of Obesity
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21760/jaims.9.6.1Keywords:
Obesity, Sthaulya, Over weight, accumulation of fat, Obenyl Tablet, AyurvedaAbstract
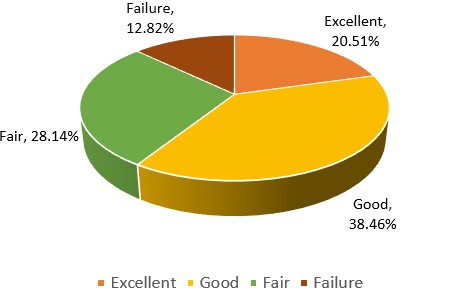
Obesity, defined as abnormal or excessive fat accumulation, which may impair health, is measured by body mass index (BMI) ≥ 30 kg/m2. In the Asian population, the BMI cut-off of obesity is lower (≥27.5 kg/m2).[1] Prevalence rate of Obesity across the globe is alarmingly increasing, irrespective of geographical areas, race, sex and age. Obesity is associated with increased risk of morbidities such as systematic inflammation, insulin resistance, and lipid abnormalities, leading to various non-communicable diseases, including cerebrovascular and cardiovascular diseases and cancer.[2] To overcome such major concern and address this issue with safer and herbal solution Charak Pharma Pvt. Ltd’s, Obenyl Tablet was taken for this Clinical Evaluation study. The study was done on 113 patients with BMI in between 28 to 40. The study is open labelled controlled single arm study. Participants were given Obenyl tablet and allowed to consume regular diet. The study shows Excellent - 20.51% (15 patients), Good - 38.93% (30 patients), Fair - 28.31% (22 patients), Failure - 12.82% (10 patients). Study shows Mean Weight Loss of 3.33Kg at the end of the study. The present study showed the therapeutic results on Completion of 120th Day in comparison to 0 Day, as Obenyl Tablet has showed 87.18% good results.
Downloads
References
Rajat Das Gupta 1, Nowrin Tamanna et al. Obesity and Abdominal Obesity in Indian Population. Epidemiologia 2023, 4, 163–172.
Kamel Ajlouni1 et al, An alarmingly high and increasing prevalence of obesity in Jordan, Epidemiol Health 2020;42,
Global Health Complications of Obesity, 2020
Abdulmoein E. Al-Agha et al : Correlation between obesity and emotional, social, and behavioral problems associated with physical limitation among children and adolescents in Western Saudi Arabia
Kiran K. Panuganti et al. Obesity - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/obesity/diagnosis,
http://ecoursesonline.iasri.res.in/mod/page/view.php?id=21871Normal and Therapeutic Nutrition 3(2+1) Lesson 31: Overweight and Obesity – causes, symptoms and dietary management
Dr Katherine M. Flegal, et al. Association of All-Cause Mortality With Overweight and Obesity Using Standard Body Mass Index Categories, JAMA. 2013 Jan 2; 309(1): 71–82.
GODA A et al, Obesity and Overweight in Asian People, Circulation Journal Vol.80, December 2016,
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/obesity/
A Kersten, Sander. Mechanisms of nutritional and hormonal regulation of lipogenesis. 2001. EMBO reports, 2:4:282-286. https://doi.org/10.1093/embo-reports/kve071
Porter SA, Massaro JM, Hoffmann U, Fox CS (2009) Abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue: a protective fat depot? Diab Care 32(6):1068–1075
Podder K, Kolge S, Benzman L, Mullin G, Cheskin L (2011) Nutraceutical supplements for weight loss: a systemic Review. Nutr Clin Pract 26(50):539–552
Nawrot P, Jordan S, Leonard S (2013) Effects of caffeine on human health. Food Addit Contam 20(1):1–30
Eric E, Berg DC (2010) The 7 principles of fat burning, 1st edn. Blackwell Science, Oxford
Nawrot P, Jordan S, Leonard S (2013) Effects of caffeine on human health. Food Addit Contam 20(1):1–30
Paul CB (2009) Nutrients that speed fat loss and why you should get them in your diet, 18th edn. McGraw-Hill, Boston
Paul CB (2009) Nutrients that speed fat loss and why you should get them in your diet, 18th edn. McGraw-Hill, Boston