Clinical evaluation of efficacy of Pilief Tablet and Pilief Ointment in the treatment of Piles
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21760/jaims.10.6.5Keywords:
Piles, haemorrhoids, herbal medicine, tablet, ointment, efficacy, clinical trialAbstract
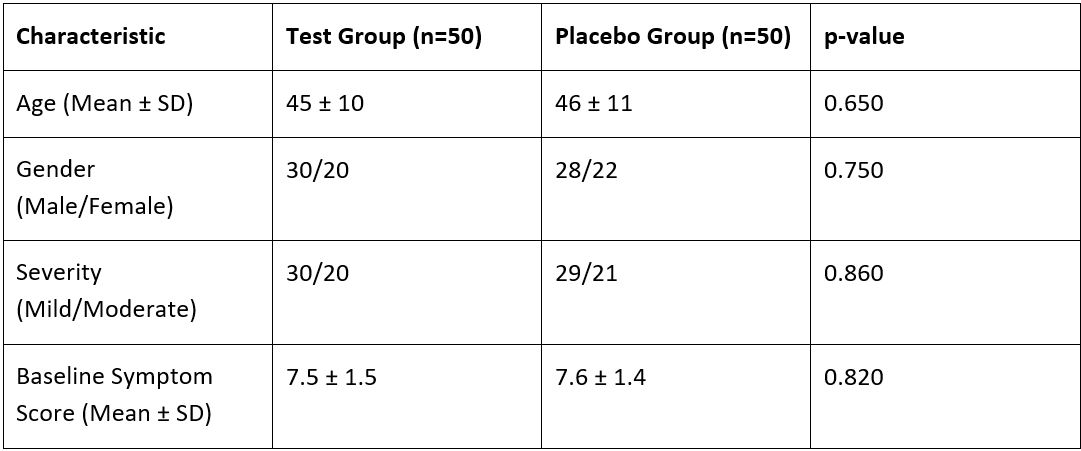
Piles, or haemorrhoids, are a common affliction that affects a significant portion of the population and is often characterized by painful symptoms that can greatly impact quality of life. Despite the availability of various pharmacological treatments, there is a growing interest in alternative therapies, particularly herbal remedies. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of a combined Pilief Tablet and Ointment in the treatment of piles. A total of 100 participants diagnosed with mild to moderate piles were enrolled in a randomized clinical trial and were treated with the Pilief Tablet and Ointment combination for six weeks. Primary outcomes included the reduction of symptoms, measured through a standardized symptoms score, and secondary outcomes included any adverse effects and quality of life assessments. Results indicated a significant reduction in symptoms and improvement in quality of life among participants. This study supports the potential of Pilief Tablet and Pilief Ointment treatments as effective options in managing piles.
Downloads
References
Kaur G, Alam MS, Athar M. Nimbidin suppresses functions of macrophages and neutrophils: relevance to its anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Phytother Res. 2004 May;18(5):419–24.
Chattopadhyay RR. Possible biochemical mode of anti-inflammatory action of Azadirachta indica A. Juss. in rats. Indian J Exp Biol. 1998 Apr;36(4):418–20.
Pillai NR, Santhakumari G. Anti-arthritic and anti-inflammatory actions of nimbidin. Planta Med. 1981 Sep;43(9):59–63.
Mehta JH, Kulkarni CG, Jadhav ST, Deshpande AM, Bhise SB. Evaluation of Indian herbs for haemostatic activity. Int J Res Pharm Chem. 2013;3(4):743–7.
Chaudhari SK, et al. An overview on Acacia catechu. Int J Res Rev Pharm Appl Sci. 2012;2(2):342–6.
Burnett BP, Jia Q, Zhao Y, Levy RM. A medicinal extract of Scutellaria baicalensis and Acacia catechu acts as a dual inhibitor of cyclooxygenase and 5-lipoxygenase to reduce inflammation. J Med Food. 2007;10(3):442–51.
Mahor G, et al. Recent update on the medicinal properties and use of Aloe vera in the treatment of various ailments. Biosci Biotech Res Commun. 2016;9(2):273–88.
Palkhade R, Jangade CR. Screening of analgesic and antipyretic activity of aqueous and alcoholic extracts of Aloe vera Linn. Vet Res Int. 2016;3(2):xx–xx. (Page numbers not provided)
Eshghi F, Hosseinimehr SJ, Rahmani N, Khademloo M, Norozi MS, Hojati O. Effects of Aloe vera cream on posthemorrhoidectomy pain and wound healing: results of a randomized, blind, placebo-control study. J Altern Complement Med. 2010 Jun;16(6):647–50.
Mard SA, Veisi A, Gharib Naseri MK, Mikaili P. Spasmogenic activity of the seed of Terminalia chebula Retz in rat small intestine: in vivo and in vitro studies. Malays J Med Sci. 2011 Jul–Sep;18(3):18–26.
Mehra R, Makhija R, Vyas N. Role of Terminalia chebula on gastrointestinal mucosa. Res J Pharm Technol. 2012;5(9):1183–6.
Mandavkar YD, Jalalpure SS. A comprehensive review on Plumbago zeylanica Linn. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol. 2011 Dec 30;5(25):2738–47.